|
IN EGYPT… |
ELSEWHERE IN THE WORLD… | |
| Narmer (Menes) conquers the Nile Valley up to the Mediterranean
Aha founds the city of Memphis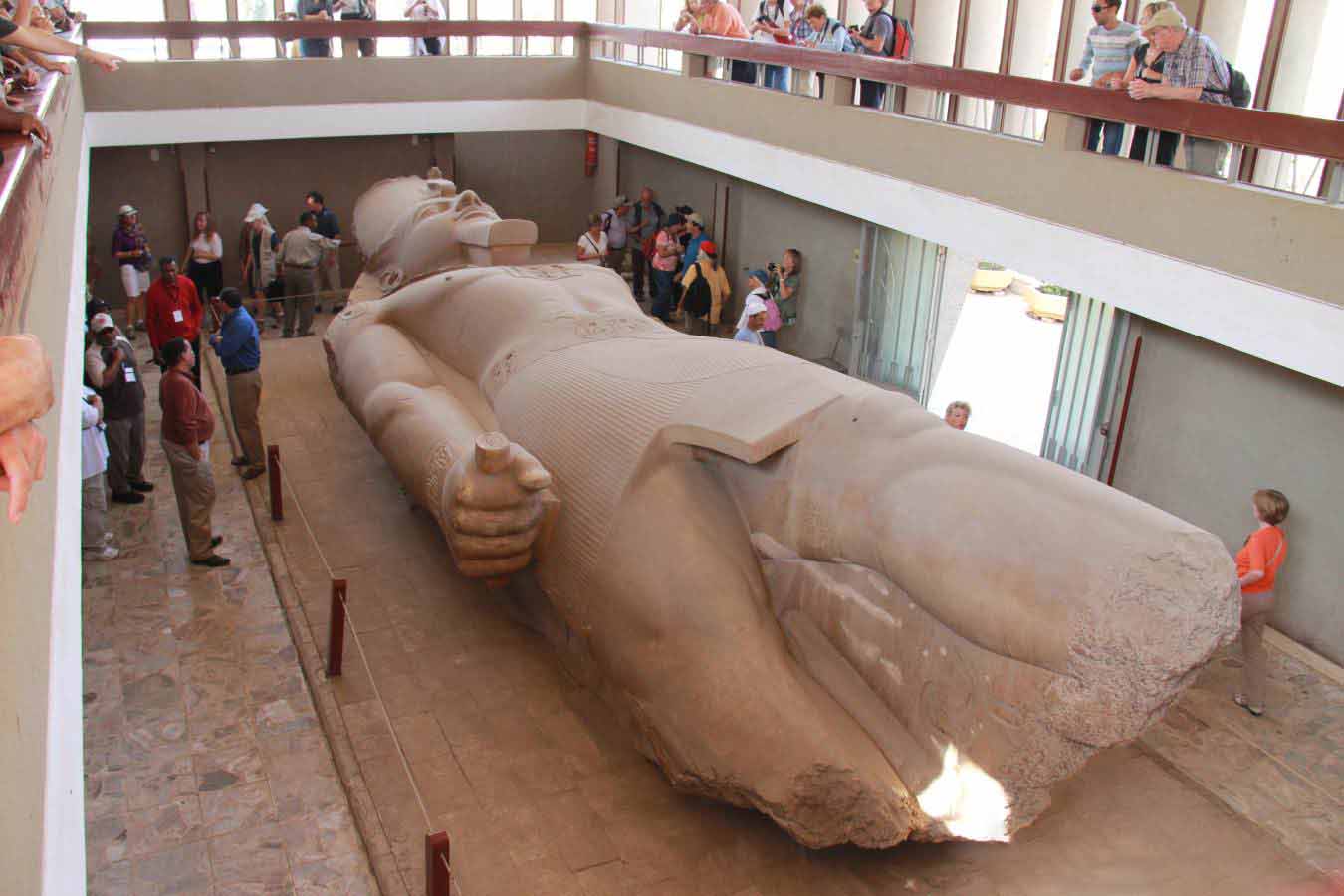  Uadji leads an expedition into the Sinai |
3000 BCE
| Cultures of Uruk, Mari, and Susa in Mesopotamia
Development of Jericho in Palestine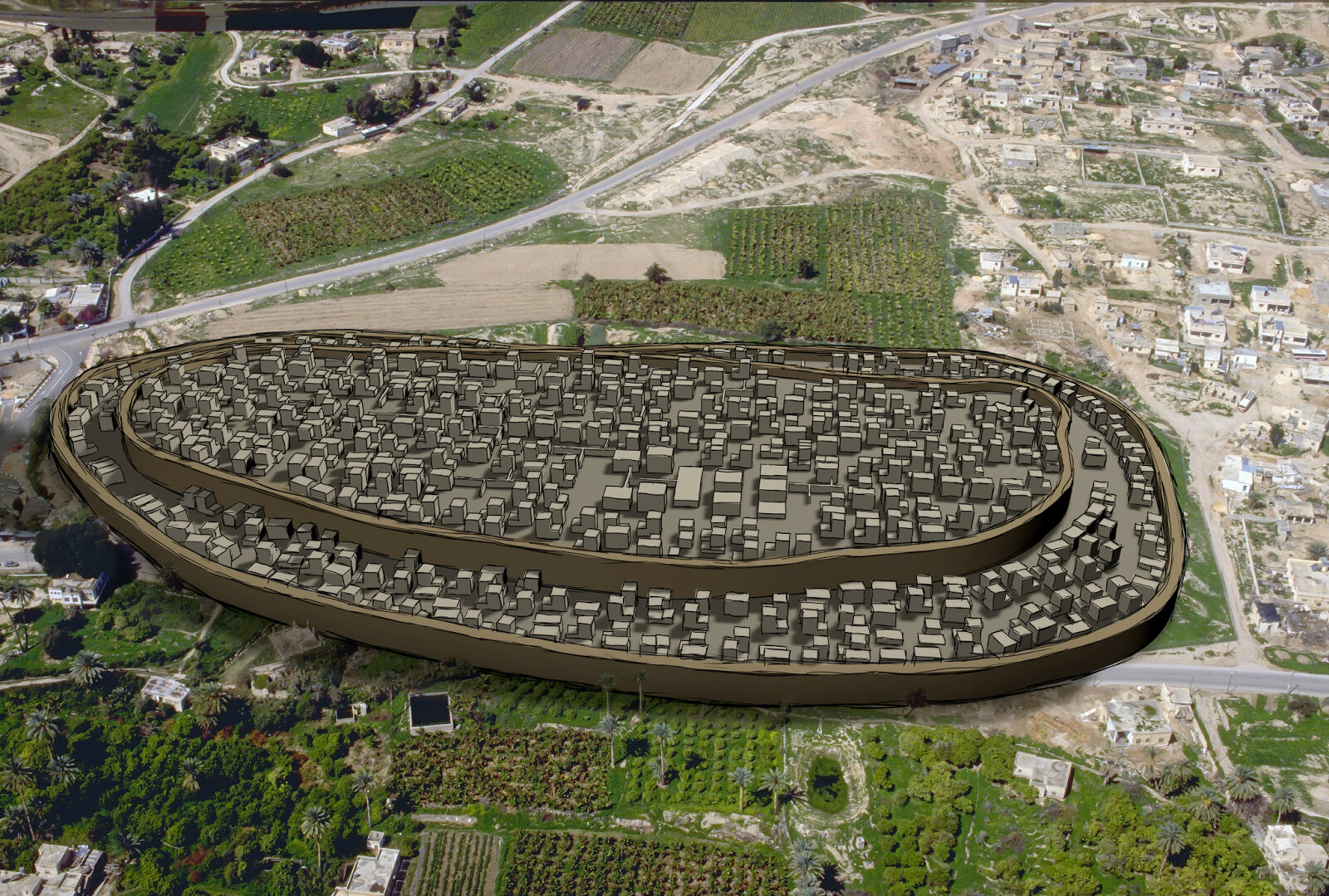  |
| Peribsen moves the capital to Memphis
Khasekhemui proclaims the cult of Horus as the highest religion with the seat of power at Heliopolis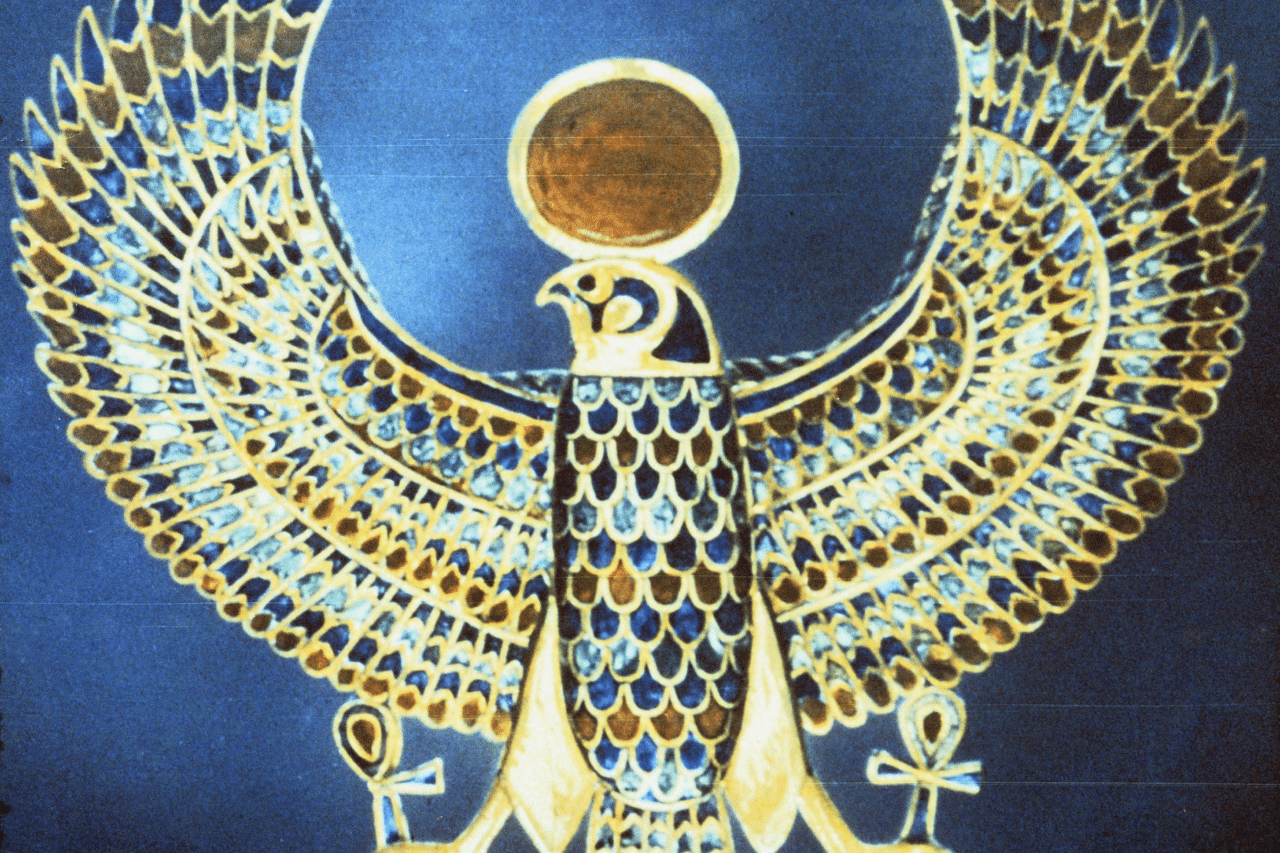  |
2850 BCE
| Ancient Minoan culture in the Aegean
Founding of Tyre and Byblos in Syria come under the Egyptian protectorate |
| Zoser identifies worship of the sun god with worship of the king. His high priest at Heliopolis, Imhotep, is first great physician and architect in history; construction in Saqqara of mausoleum-city of Zoser centered on large stepped pyramid
Sekhemkhet has fortresses built along all frontiers Khaba, last king of the 3rd dynasty |
2770 BCE
| Beginning of the golden age of the Sumerians of Ur and Lagash; temples and palaces are built of brick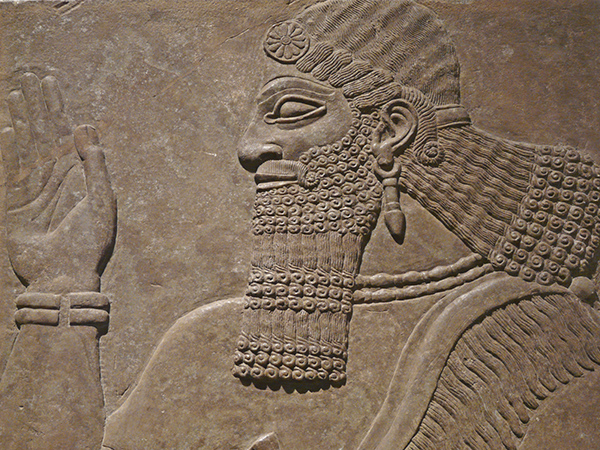 |
| Snefru is remembered as a kind and humane pharaoh; builds first smooth-faced pyramid
Khufu (Cheops) builds first great pyramid  Khafre builds second great pyramid with mortuary temple and granite valley temple Menkaure (Mycerinus) builds smallest of the great pyramids |
2620 BCE
| Development of Troy I
First temples at Ashur; temple of Ishtar and of Samak at Mari  |
Userkaf builds pyramid at Saqqara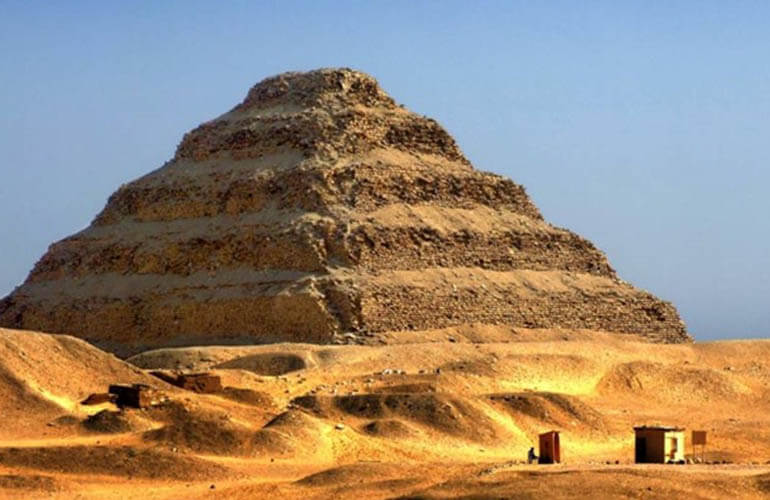 
Sahura digs canal of Bubastis joining Mediterranean with the Red Sea Unas builds a pyramid, decorating the interior with the “Pyramid Texts” and “Wisdom of Ptah-Hotep,” two of the most important Egyptian texts |
2500 BCE
| Beginning of King Sargon’s Akkadian Empire in Mesopotamia; the dynasty rules for about two centuries  |
| Pepi I witnesses the decline in royal power with increase in the power of the princes
Pepi II, with the longest reign in Egyptian history (94 years)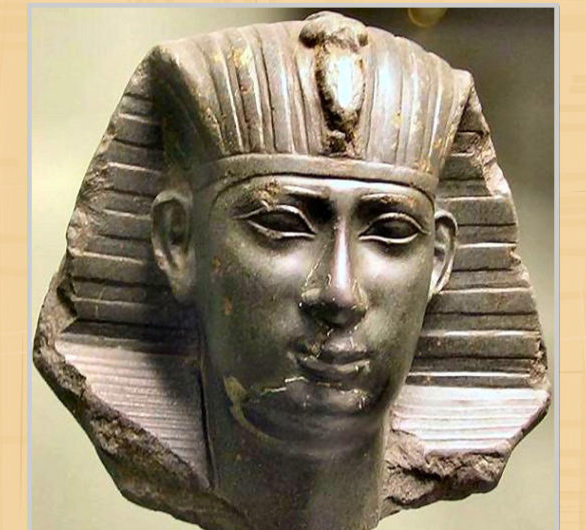  |
2350 BCE
| Beginning of the Gutian dynasty in 2240; ziggurat of Ur is built |
| Neferkare installs a monarchy as “God given” but not divine; the king is primus inter pares among the princes, but not all princes recognize him |
2180 BCE
| Development of Troy II, III, IV
Development of Minoan culture in the Aegean  Sumerians regain their independence with the third dynasty of Ur |
Sehertani-Antef, self-appointed king, shifts power to Thebes |
2120 BCE
| Middle Minoan culture in the Aegean |
| Sesostris I (Senusret) is the first pharaoh to introduce co-regency with his son to ensure dynastic continuity
Amenemhet II extends the empire as far as Megiddo in Palestine Amenemhet III builds an imposing residence in the Fayyum, the “Labyrinth” |
1991 BCE
| End of 3rd dynasty of Ur in Mesopotamia
First palaces of Knossos and Phaestot in the Aegean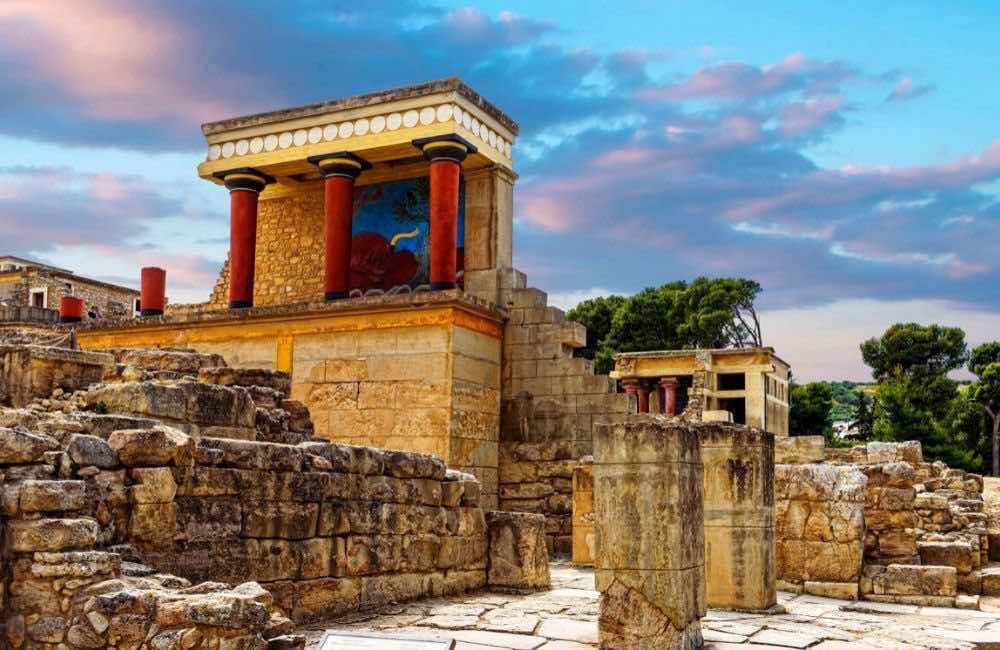  |
| Sekhemre marries the ruling regent and assumes part of her power; Nubia withdraws from Upper Egypt |
1785 BCE
| Reign of Hammurabi in Babylonia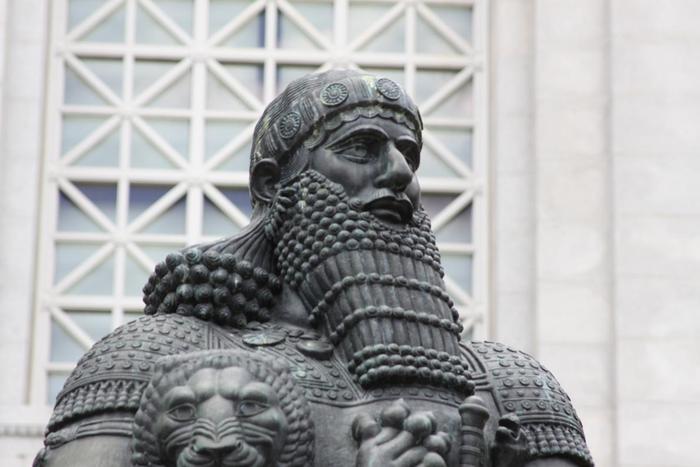  Development of art |
Neferhotep carries the protectorate to Byblos in Lebanon; the Hyskos invade the fertile Delta land, bringing the horse and the wheel and the cult of the god Baal |
1745 BCE
| Invention of the alphabet in Phoenicia 
Indo-Europeans move down towards India and Persia |
Ahmose reconquers Nubia to Abu Simbel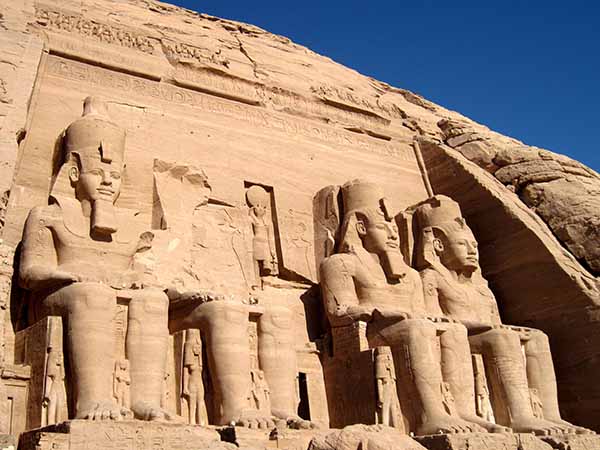 |
1622 BCE
| Beginning of the Hittite empire in Asia Minor  Shang dynasty and culture in China
|
| Amenophis I extends the frontiers to the Euphrates River and clashes with the Hittites
Thutmosis I takes Thebes to its maximum splendor; the temple at Karnak is enriched with pylons and obelisks; the Great Hypostyle Hall is raised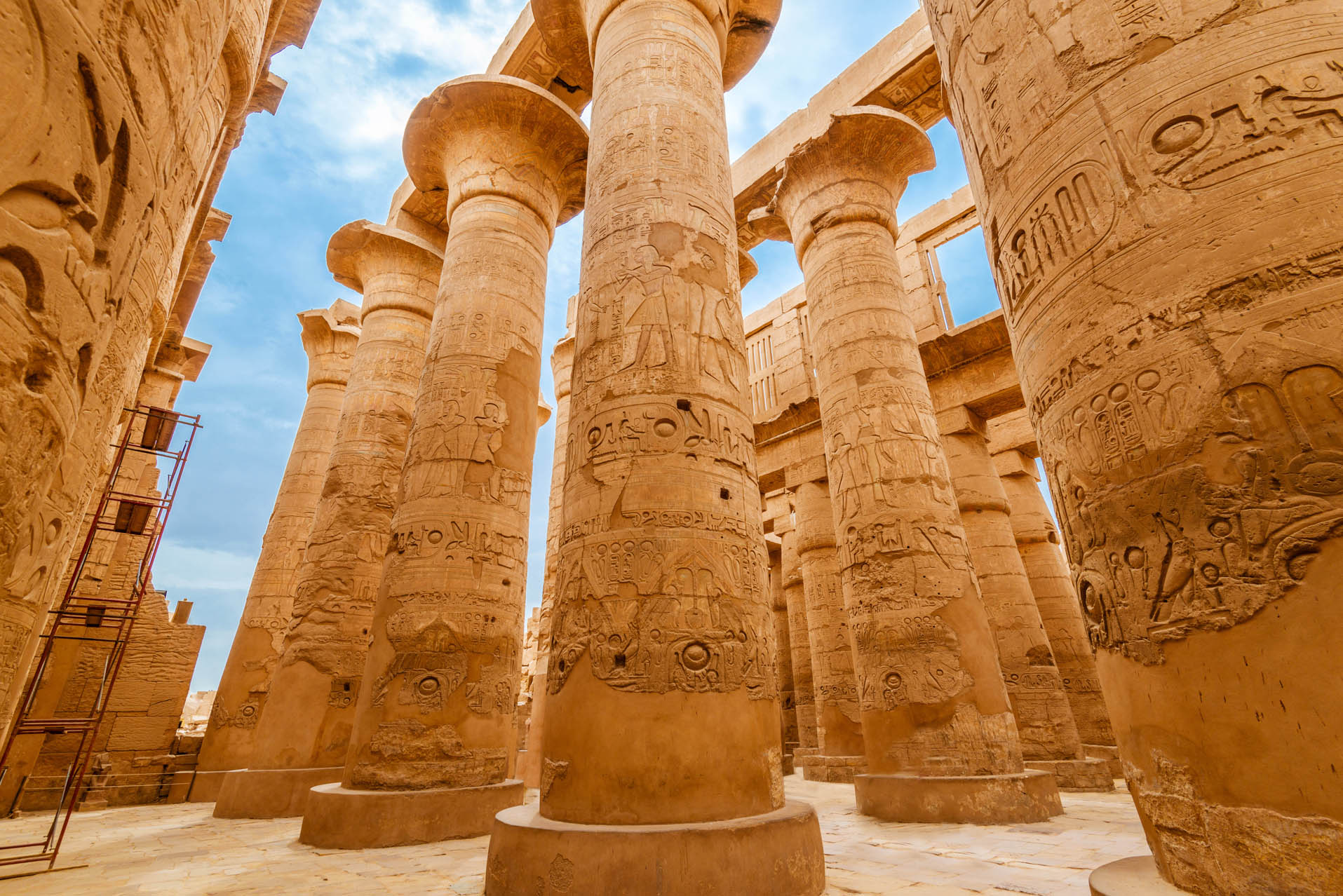  Thutmosis II marries half-sister Hatshepsut Hatshepsut reigns for 20 years as regent for her son, wears male attire and false beard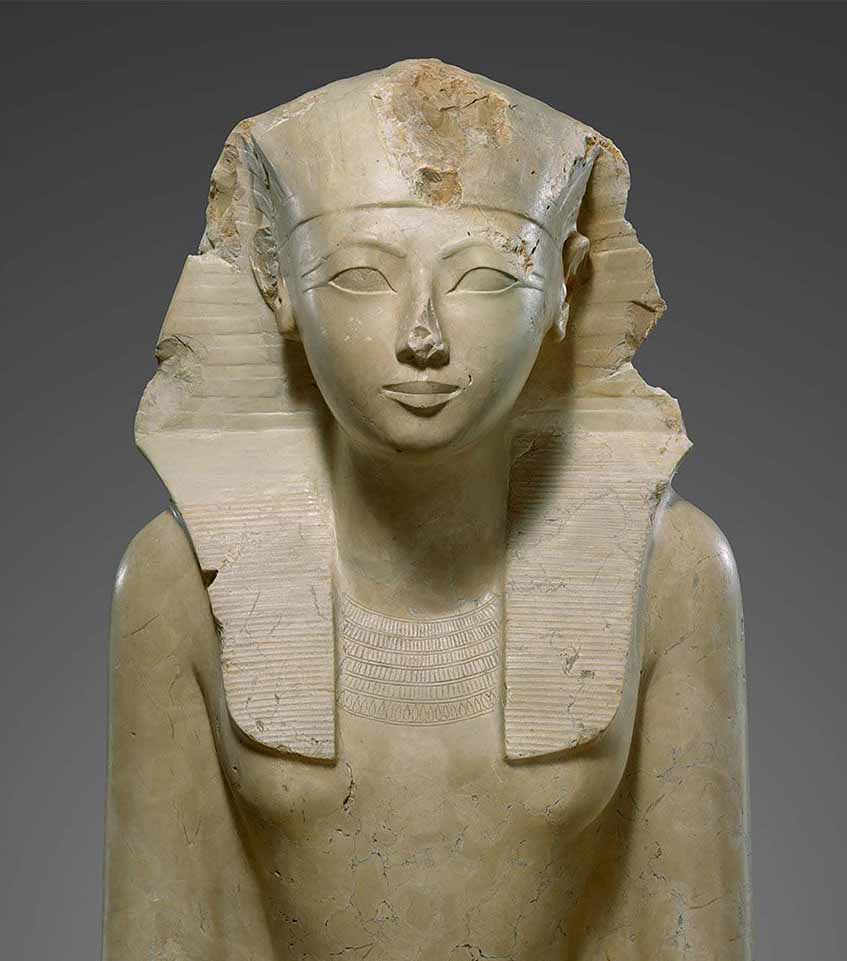  Thutmosis III defeats the Mitanni at Kadesh; extends his dominion to Crete and Cyprus; Egyptian art and culture spread throughout the world Akhenaten and wife Nefertiti replace the polythestic religion of Amon with worship of a single god, Ra (the sun)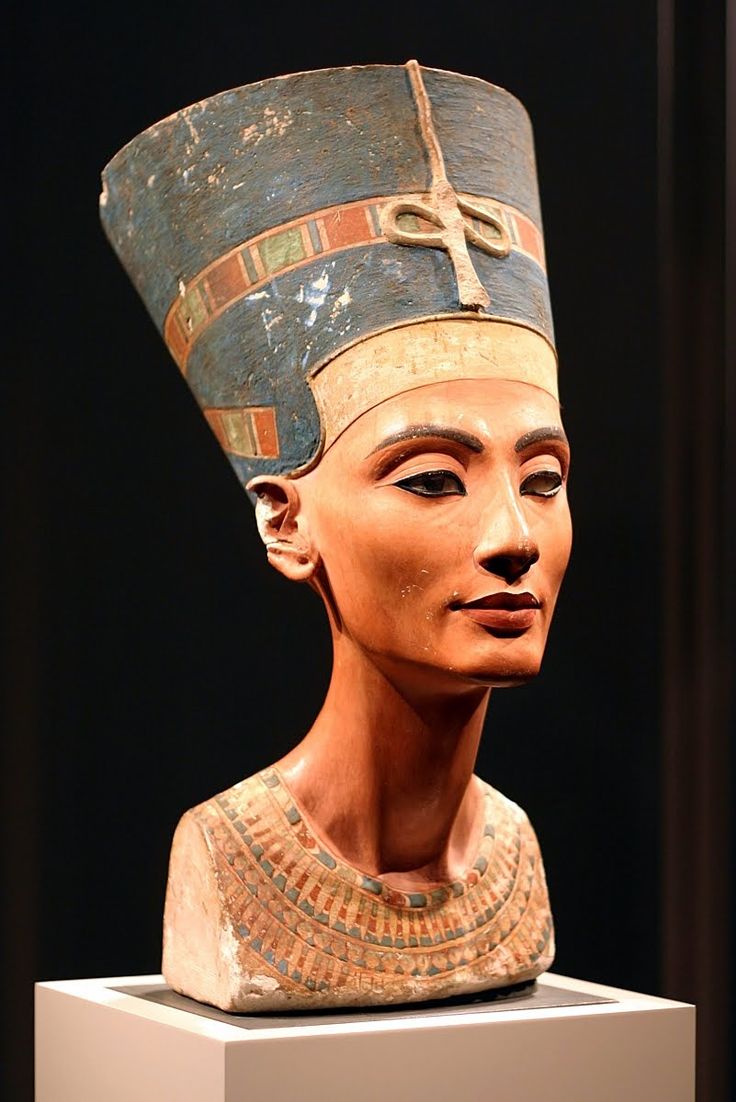  Tutankhamun re-establishes cult of Amon, but dies at age 18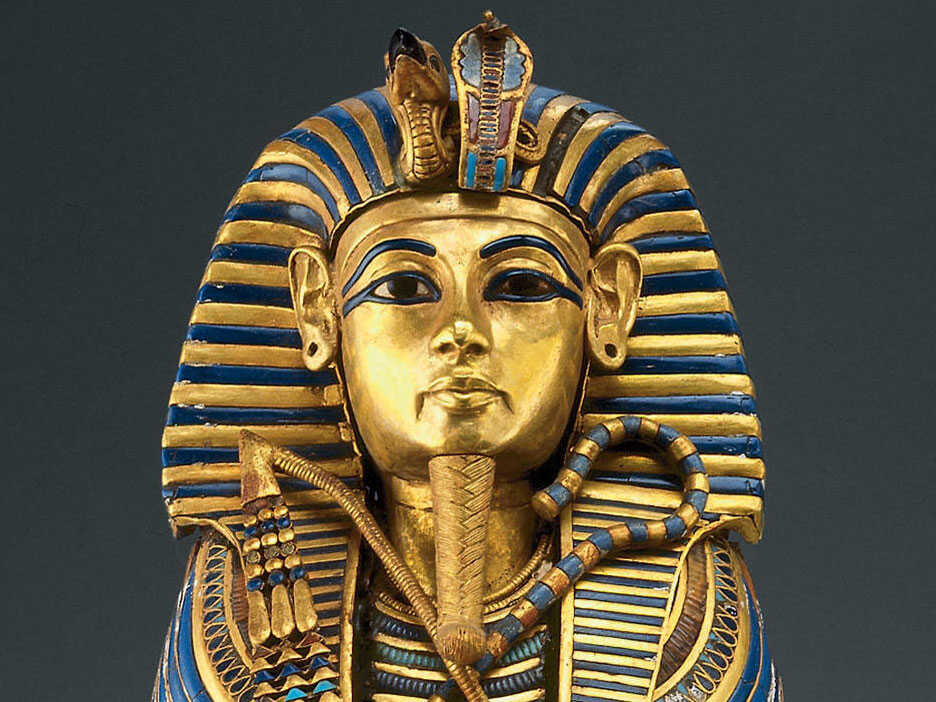  Horemheb destroys all traces of one-god religion | 1580 BCE | Legendary kingdom of Minos in Crete
Expansion of the Hittite empire in Asia Minor The Kassites conquer Babylonia in Mesopotamia Zenith of Mycenean culture in Greece: beehive tombs, Lion’s Gate  Beginning of middle Assyrian empire in Asia Minor Shang dynasty in China |
| Ramses I comes to power and moves the capital to Tanis
Seti I drives back the Hittites, takes back Phoenicia, and occupies Kadesh Ramses II takes the royal residence to Avaris; signs first historical international treaty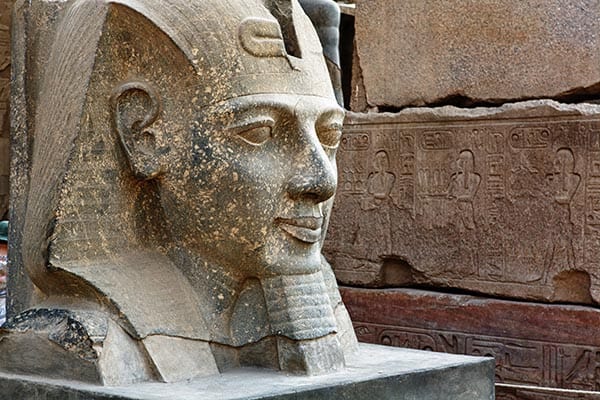  Seti II defends the Delta from Libyan invasions | 1314 BCE | Epic Trojan war begins in 1280 
Beginning of the Ionian immigration in the Aegean |
| Ramses III continues to restore empire; assassinated by corrupt members of his own staff
Ramses IX tries to wrestle power away from the priests of Amon | 1200 BCE | Beginning of protogeometric art in Greece |
| Mendes governs lower Egypt from Tanis | 1085 BCE | Reign of Saul, and then David, in Palestine |
| Shesonq I, after the death of King Solomon, renews campaign to conquer Palestine | 950 BCE | Zenith of Israel with the building of the Temple of Jerusalem by King Solomon, who later marries an Egyptian princess |
| Tefnakhte conquers Hermopolis and recovers part of lower Egypt
Bocchoris forms a peace with the Assyrians; raises workers and lower middle classes | 730 BCE | Beginning of the Olympic Games in Greece 
Founding of Rome  |
| Piankhi annexes upper Egypt to Nubia
Shabaka moves capital back to Thebes Tanutamon is overwhelmed by an Assyrian invasion which sacks Thebes | 716 BCE | Beginning of Chou dynasty of art in China
Beginning of Corinthian art in Greece; Greek philosopher Pythagoras  |
| Psamtik I (Psammetichus) conquers the Delta and places friends and relatives in key positions
Necho II reconstructs the Red Sea canal  Psamtik II reconquers Nubia and the gold mines; the pharaoh is no longer a son of Osiris — his power rests solely with the people | 666 BCE | Beginning of Etruscan art in Italy
Destruction of Nineveh and the end of the Assyrian empire in Mesopotamia Beginning of the reign of Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylonia; ziggurat and palace with hanging gardens; gates of Ishtar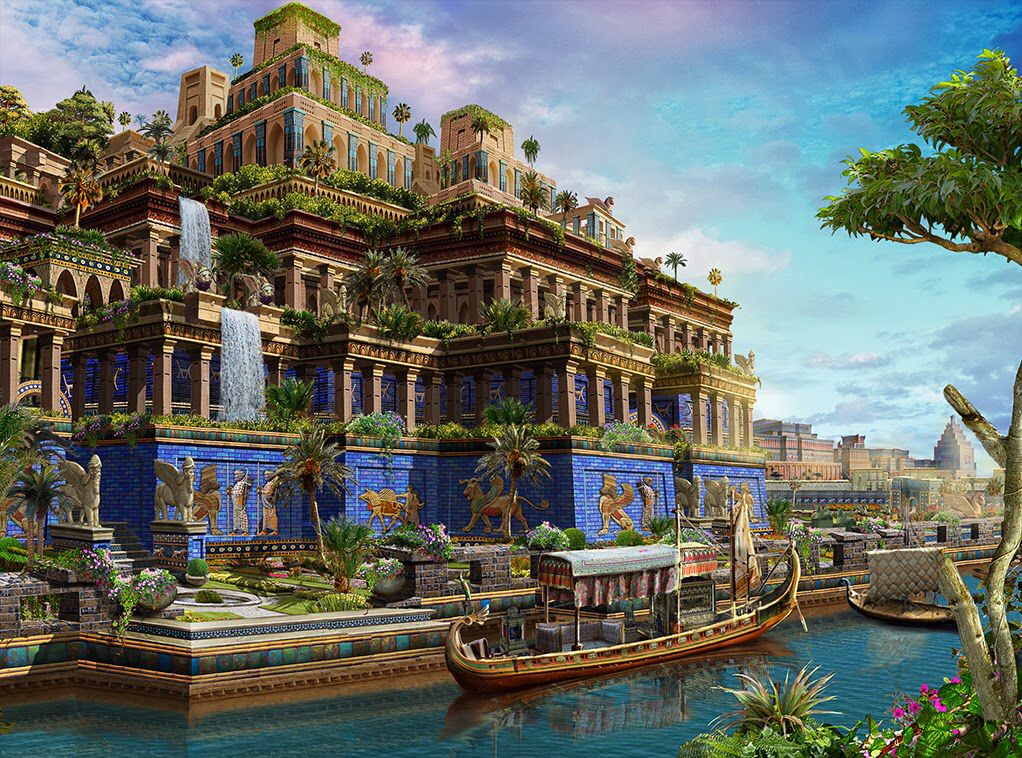  Destruction of Jersalem and the Temple of Solomon |
| Cambyses, after conquering Egypt, is crowned at Sais and consecrated at Heliopolis
Darius I reorganizes Egyptian economy; once again opens up the Red Sea canal to join the Mediterranean Sea and Indian Ocean Xerxes puts down two revolts in lower Egypt  Darius II puts down a third revolt | 524 BCE | Preaching of the Buddha in India Dialogues of Confucius and Lao-Tse in China Persian wars and defense of Thermopoliae in Greece Era of Pericles in Greece; peace with Persia, treaty with Sparta, great acropolis of Athens is built  |
Nephritis I, head of the Egyptian army, takes over power
Nectanebo II takes over the vascillating power, but when betrayed by Greek mercenaries, flees into Upper Egypt Kabbas is nominated pharaoh by priests at Memphis Darius III reconquers Egypt Alexander the Great drives the Persians from Egypt; recognized as the son of Ra by the oracle at Luxor; founds a new capital at Alexandria, which becomes the economic and cultural center for the entire ancient world  | 398 BCE | Roman expansion; Camilus drives back the Gauls
Philip of Macedon invades Greece; his son, Alexander the Great, conquers the Persian empire, Egypt, and continues up to the Indus River  Philosophy of Plato and Aristotle |
Ptolemy I Soter declares himself king of Egypt and founds the city of Ptolemais, near Thebes Ptolemy II Philadelphus takes back Cyprus, Tyre, and Sidon and signs a friendship pact with Rome Ptolemy V Epiphanes obtains Syria as dowry of Cleopatra I, given to him as wife by King Antiochus Ptolemy XIII Neos Dionysos has Pompey assassinated to ingratiate himself with Caesar, the new absolute lord of Rome. On a visit to Egypt, Caesar marries Cleopatra VII, (sister of Ptolemy) and the two dream of the union of Rome and Egypt; they have a son, Caesarion  Cleopatra VII, on Caesar’s death, tries to revive the Egyptian economy with the help of Antony; Caesarion becomes pharaoh; Rome declares war on Egypt, and under mounting pressure, Cleopatra and Antony commit suicide | 311 BCE 44 BCE | Empire of the Selucids in Mesopotamia
Construction of the first stupas in India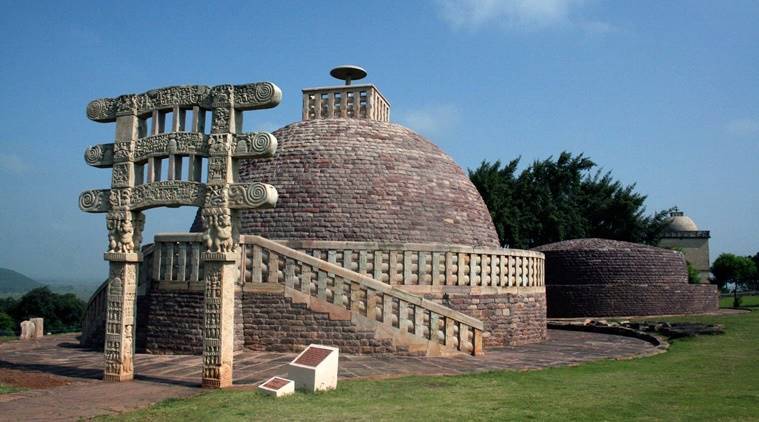  First and Second Punic wars between Rome and Carthage in Italy; expansion of Rome in the Mediterranean Building of Great Wall of China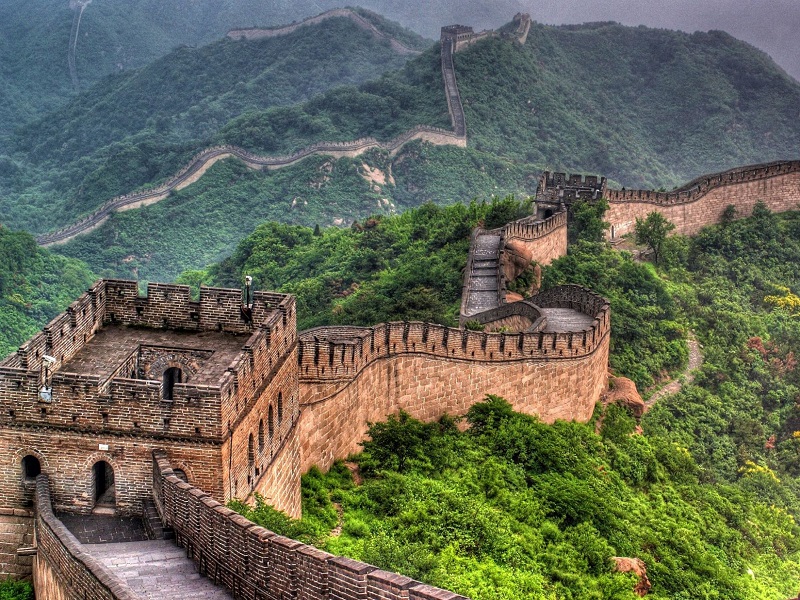  Third Punic War — Rome destroys Carthage and conquers Greece, Asia Minor, and Tunisia Rome draws up political and economic relationship with Egypt |
| 0 | Conventional date of the birth of Jesus in Nazareth | |
| Nero restores and renovates monuments but also organizes expeditions to find the source of the Nile | 54 A.D. | |
Trajan reactivates the ancient canal leading from Bubastis to the Red Sea (much of this route becomes present-day Suez Canal) | 98 A.D. | |
| Hadrian founds the city of Antinoe, visits the Colossi of Memnon and the Temples at Thebes | 117 A.D. | Work is begun on Hadrian’s Wall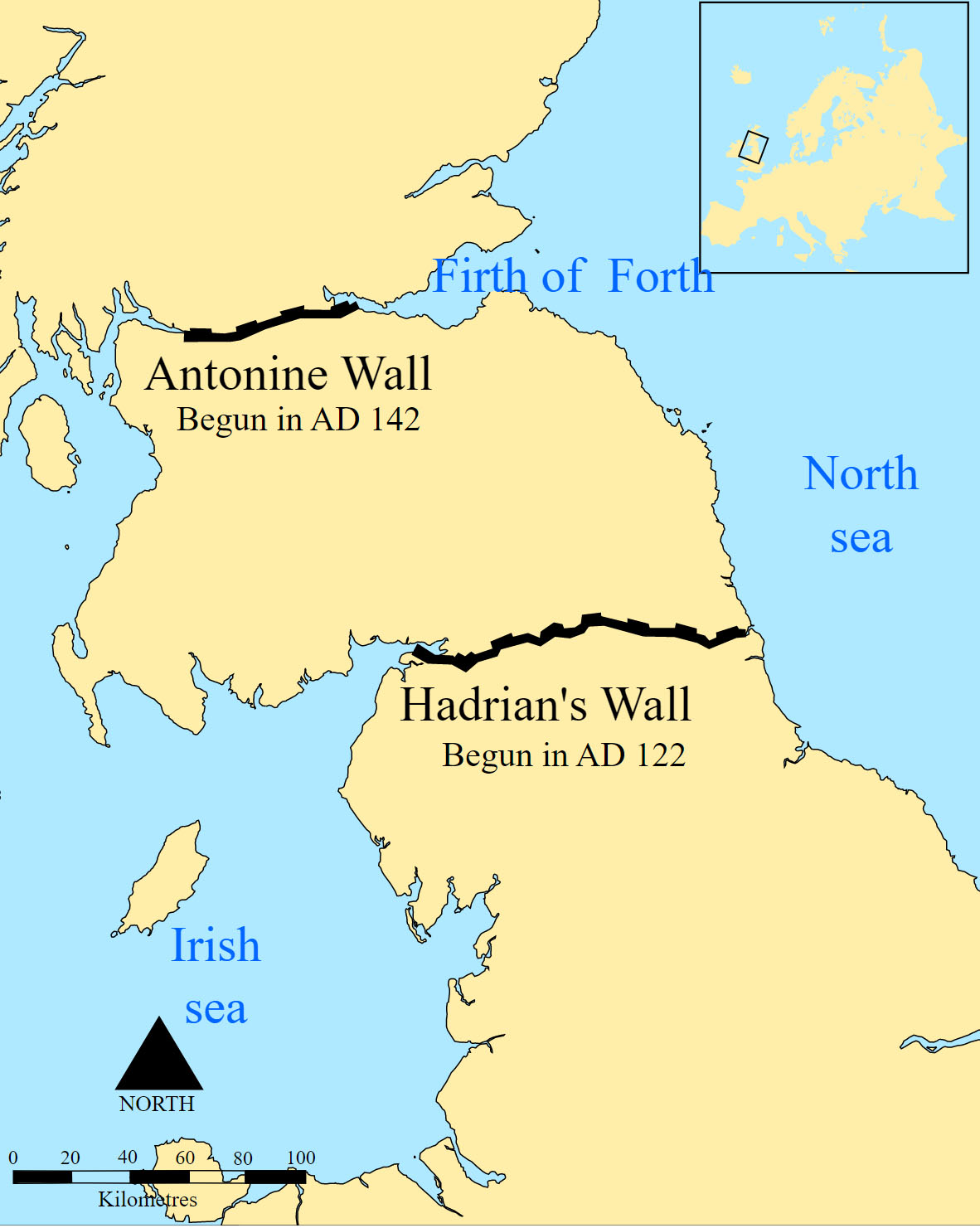 |
Treasures of Egypt Tours, LLC
(769) 232-1775 * info@treasuresofegypttours.com

